UGC-NET NOVEMBER 2017 QUESTIONS WITH EXPLANATION
NTA-NET NOVEMBER 2017 QUESTIONS WITH EXPLANATION
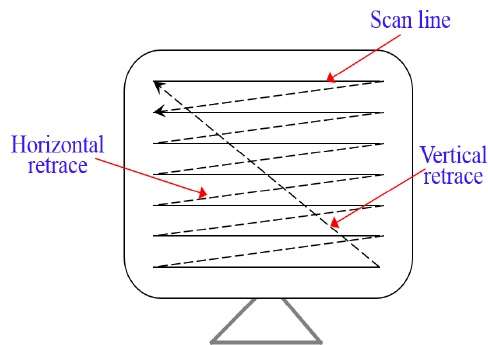
Q:15 With respect to CRT, the horizontal retrace is defined as:
(A) The path an electron beam takes when returning to the left side of the CRT.
(B) The path an electron beam takes when returning to the right side of the CRT.
(C) The technique of turning the electron beam off while retracing.
(D) The technique of turning the electron beam on/off while retracing.
Answer: (A)
Explanation: In computer graphics Horizontal Retrace is defined as: The path an electron beam takes when returning to the left side of the CRT.