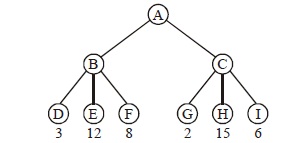
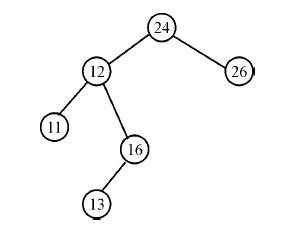
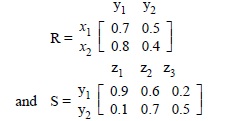UGC-NET JULY 2016 PAPER 1 SET-A QUESTIONS WITH EXPLANATION
Q:: 1. Select the alternative which consists of positive factors contributing to effectiveness of
teaching :
Q:: 5 A researcher intends to explore the effect of possible factors for the organization of effective mid-day meal interventions. Which research method will be most appropriate for this study ?
Q:: 1. Select the alternative which consists of positive factors contributing to effectiveness of
teaching :
List of factors :
(a) Teacher’s knowledge of the subject.
(b) Teacher’s socio-economic background.
(c) Communication skill of the teacher.
(d) Teacher’s ability to please the students.
(e) Teacher’s personal contact with students.
(f) Teacher’s competence in managing and monitoring the classroom transactions.
Codes :
(1) (b), (c) and (d) (2) (c), (d) and (f)
(3) (b), (d) and (e) (4) (a), (c) and (f)
Answer::(4)
(a) Teacher’s knowledge of the subject.
(b) Teacher’s socio-economic background.
(c) Communication skill of the teacher.
(d) Teacher’s ability to please the students.
(e) Teacher’s personal contact with students.
(f) Teacher’s competence in managing and monitoring the classroom transactions.
Codes :
(1) (b), (c) and (d) (2) (c), (d) and (f)
(3) (b), (d) and (e) (4) (a), (c) and (f)
Answer::(4)
Q::2 The use of teaching aids is justified on the grounds of
(1) attracting students’ attention in the class room.
(2) minimising indiscipline problems in the classroom.
(3) optimising learning outcomes of students.
(4) effective engagement of students in learning tasks.
Answer::(3)
(1) attracting students’ attention in the class room.
(2) minimising indiscipline problems in the classroom.
(3) optimising learning outcomes of students.
(4) effective engagement of students in learning tasks.
Answer::(3)
Q:: 3 Assertion (A) :
The purpose of higher education is to promote critical and creative
thinking abilities among students.
thinking abilities among students.
Reason (R) :
These abilities ensure job placements.
Choose the correct answer from the following code :
(1) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(2) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(3) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(4) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer::(2)
Q:: 4 Match the items of the first set with that of the second set in respect of evaluation system.
Choose the correct code :
Set – I Set – II
a. Formative evaluation i. Evaluating cognitive and co-cognitive
aspects with regularity
b. Summative evaluation ii. Tests and their interpretations based on a
group and certain yardsticks
c. Continuous and comprehensive evaluation iii. Grading the final learning outcomes
Choose the correct answer from the following code :
(1) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(2) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(3) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(4) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer::(2)
Q:: 4 Match the items of the first set with that of the second set in respect of evaluation system.
Choose the correct code :
Set – I Set – II
a. Formative evaluation i. Evaluating cognitive and co-cognitive
aspects with regularity
b. Summative evaluation ii. Tests and their interpretations based on a
group and certain yardsticks
c. Continuous and comprehensive evaluation iii. Grading the final learning outcomes
d. Norm and criterion referenced tests iv. Quizzes and discussions
Codes :
a b c d
(1) iv iii i ii
(2) i ii iii iv
(3) iii iv ii i
(4) i iii iv ii
Codes :
a b c d
(1) iv iii i ii
(2) i ii iii iv
(3) iii iv ii i
(4) i iii iv ii
Answer::(1)
(1) Historical method (2) Descriptive survey method
(3) Experimental method (4) Ex-post-facto method
Answer::(4)
Q::6 Which of the following is an initial mandatory requirement for pursuing research ?
(1) Developing a research design
(2) Formulating a research question
(3) Deciding about the data analysis procedure
(4) Formulating a research hypothesis
Answer::(2)
Q:: 7 The format of thesis writing is the same as in
(1) preparation of a research paper/article
(2) writing of seminar presentation
(3) a research dissertation
(4) presenting a workshop / conference paper
Answer::(3)
Q:: 8 In qualitative research paradigm, which of the following features may be considered critical ?
(1) Data collection with standardised research tools.
(2) Sampling design with probability sample techniques.
(3) Data collection with bottom-up empirical evidences.
(4) Data gathering to take place with top-down systematic evidences.
Answer::(3)
Q:: 9 From the following list of statements identify the set which has negative implications for
‘research ethics’ :
‘research ethics’ :
(i) A researcher critically looks at the findings of another research.
(ii) Related studies are cited without proper references.
(iii) Research findings are made the basis for policy making.
(iv) Conduct of practitioner is screened in terms of reported research evidences.
(v) A research study is replicated with a view to verify the evidences from other researches.
(vi) Both policy making and policy implementing processes are regulated in terms of
preliminary studies.
preliminary studies.
Codes :
(1) (i), (ii) and (iii) (2) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(3) (ii), (iv) and (vi) (4) (i), (iii) and (v)
Answer::(3)
Q:: 10 In a research on the effect of child-rearing practices on stress-proneness of children in completing school projects, the hypothesis formulated is that ‘child rearing practices do influence stress-proneness’. At the data-analysis stage a null hypothesis is advanced to
find out the tenability of research hypothesis. On the basis of the evidence available, the
null hypothesis is rejected at 0.01 level of significance. What decision may be warranted
in respect of the research hypothesis ?
find out the tenability of research hypothesis. On the basis of the evidence available, the
null hypothesis is rejected at 0.01 level of significance. What decision may be warranted
in respect of the research hypothesis ?
(1) The research hypothesis will also be rejected.
(2) The research hypothesis will be accepted.
(3) Both the research hypothesis and the null hypothesis will be rejected.
(4) No decision can be taken in respect of the research hypothesis.
Answer::(2)
ugc net computer science question papers,ugc net computer science december 2014 question papers, ugc net computer science july 2016 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2014 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2014 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2013 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2013 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2012 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2012 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2011 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2011 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2010 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2010 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2009 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2009 question papers,
ugc net computer science june 2008 question papers,
ugc net computer science december 2008 question papers,